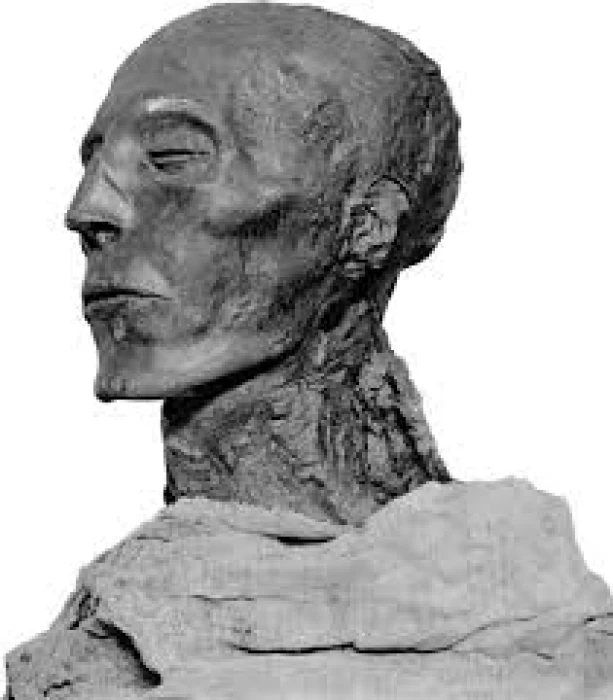
King Seti I
Details about King Seti I
Sethi I (or Sethos or Seti) is the second Pharaoh of the 19th dynasty. Manethon calls him Sethôs (Africanus, Eusebius, Flavius Josephus). He is the son of Ramses I and Queen Satre. According to specialists, it is at an age between 27 and 29 years that his father will associate him with the power as co-regent and let him lead the foreign affairs of the country.
A few monuments and a fragment of a statue would attest to this proposal. At this time he bears several titles including those of: Prince regent, Mayor of Thebes, Vizier, General of the troops of tanks of the King (Charrerie), Commander of the troops and fortifications of the fortress of Tjarou. The latter two were functions that his father was performing before he took over. Some scholars consider him the true founder of the dynasty.
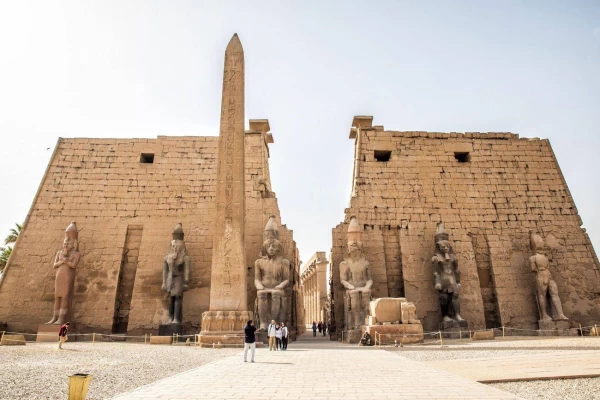
Séti does not take any special measures to increase the prosperity of Egypt. It strengthens the borders, makes new mines and quarries work, drills wells and reconstructs temples and shrines that had fallen into ruin or were damaged. He also continued the work undertaken by his father for the construction of the great hypostyle hall of the temple of Karnak, one of the most imposing monuments of Egyptian architecture.
Perhaps the most emblematic monument is the mortuary temple of Abydos, dedicated to Osiris and six other deities. It is indeed decorated with polychrome bas-reliefs of extreme delicacy that have preserved part of their original colors. Behind the temple stands a curious building that is said to be the cenotaph of Séti. The tomb of the pharaoh is the largest and best preserved in the whole Valley of the Kings.
Although his son Ramses II is more famous than he, many Egyptologists consider Seti I to be the greatest pharaoh of the 19th dynasty.















