Ancient Egyptian Social Structure
The social structure in ancient Egypt
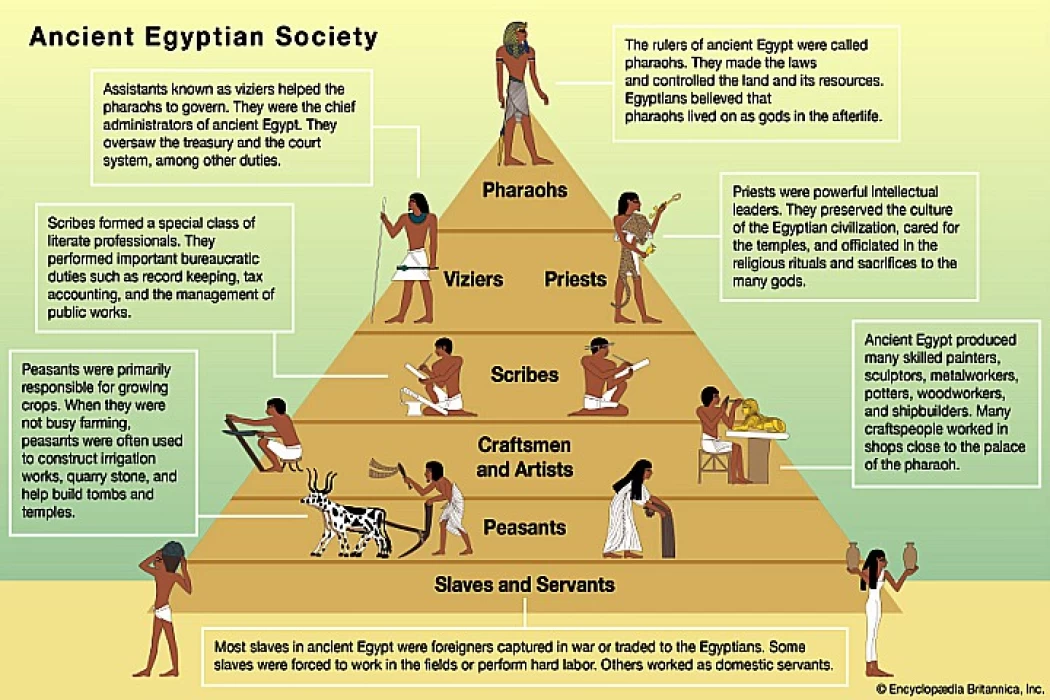
The social structure of ancient Egyptian society can be categorised into a social pyramid headed by the pharaoh and government dignitaries, followed by the class of priests and nobles, then the class of soldiers and scribes, followed by the class of craftsmen and merchants, and finally at the bottom of the pyramid are the classes of peasants and slaves, and this article will discuss each class in detail.
The pharaohs were seen as gods themselves because they were believed to be the sons of the god Ra and were therefore divine beings as well as the intermediaries between humans and other gods since they were the ones who ruled the land according to what they said, established laws, kept law and order, defended their land with standing army, cared about their subjects, satisfied the gods thus preventing the Nile from flooding or famine from occurring by controlling the regular flooding.
A vizier was the second most powerful position after the pharaoh, sometimes serving as the high priest of Amun-Ra, was installed by the pharaoh, and could last for several rulers unless the current pharaoh wanted to install a new vizier.
The nobles occupied many government positions in the state, which were available only to the ruling family, and the nobles, and the nobles rule different regions of the state, set local laws, and own agricultural lands in which the peasant class works, while priests occupied a high rank in ancient Egyptian society, and they were appointed by the pharaoh at first, but then the matter turned into heredity, and their task was to serve the gods and satisfy them by taking care of the temples, holding rituals, various celebrations in them, and making offerings to them.
Ancient Egyptian society had soldiers protecting the state, supervising laborers, and receiving spoils and gifts. Scribes, the few with literacy, kept records of army numbers, food production, construction workers, legal contracts, wills, tax, genealogical, medical procedures, and the Book of the Dead.
Among the professions in the artisan class were physicians, painters, sculptors, miners, goldsmiths, potters, carvers, weavers, and stone carvers. Merchants imported goods from overseas, such as ebony wood, cedar wood, tiger skins, giraffe tails for fly swatters, and animals for temples and palaces, including lions and baboons, and marketed the creations of artists both within and beyond the nation.
The peasant class included farmers, servants, and construction workers, whose tasks were limited to cultivating fields, raising livestock, maintaining canals and water reservoirs, working in quarries, and building royal monuments. Slaves were prisoners of war. Ancient Egyptians did not have a slave market and were forced to work in the homes of the nobility, temples, or the ruling family, as well as being forced to work in construction.
















