Ancient Egyptian Calendar
History of the egyptian calendar
The solar calendar, which the ancient Egyptians invented to divide the year into 13 months based on the sun, was the first Egyptian and global calendar in human culture. One of the first methods of measuring time that humans are said to have created is the Egyptian calendar.
According to the Gregorian calendar, the Egyptian Coptic New Year is observed today on September 11. On the eve of Nowruz, prayers are conducted in Orthodox churches all around the world. Egyptian Copts also call it Nowruz. Coptic Calendar is thought to be dated back as far as 4241 B.C, which is way earlier than the dynastic period and formation of the united Egyptian state. The ancients had already realized the existence of a lunar calendar that they further subdivided into seasons, within which were months, days and even hours, and were able even to differentiate a common year and a bissextile year something that at that time was an astronomical miracle.
What was the Egyptian calendar based on
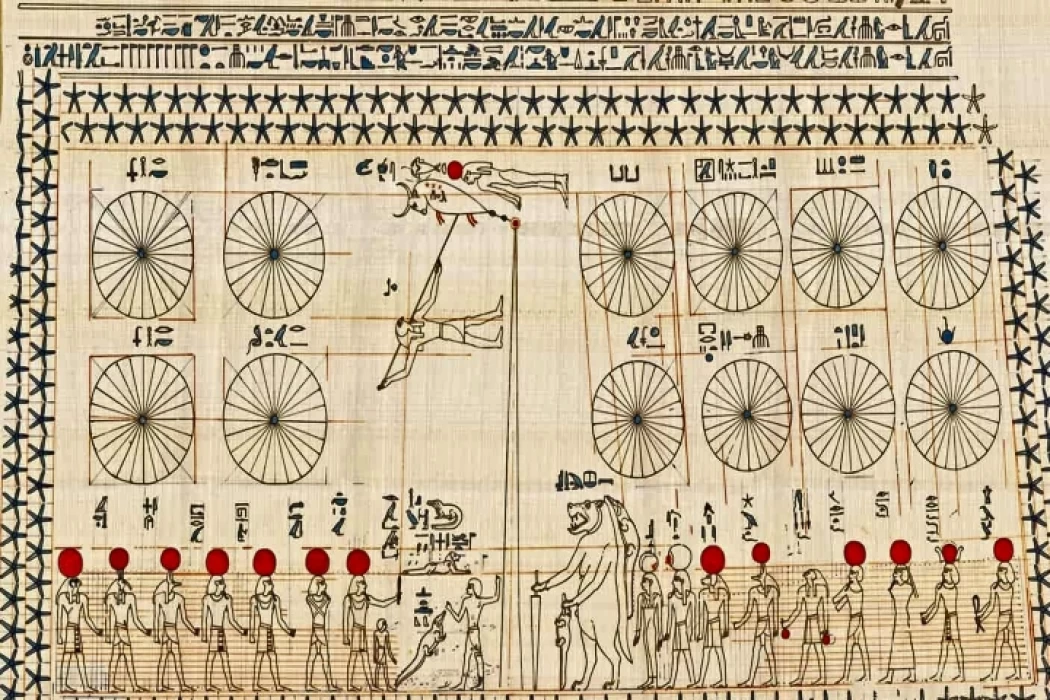
The Coptic calendar, which is also referred to as the ‘Martyrs’ Calendar’, is a descendant of the primordial Egyptian calendar which was called the astronomical calendar, a system of measuring out of the built-up years by the ancient Kenyan people as they had many structures within a year and I their structure had 13 months.
Historically, the Coptic calendar, deferring slightly to the ‘Calendar of Saints’ is rooted on the ancient Egyptian one known as a solar or star calendar is a system of Yarthri divisions on the basis of a year as used by the Egyptian ancients belonging to the genre Where the completed circle comprises 13 months.
It is considered one of the first calendars known to mankind and the most accurate in terms of climate and agricultural conditions during the year, so that the Egyptian farmer has been relying on it to determine the planting seasons and crops for thousands of years.
The Egyptian calendar contributed to the development of the various calendars of ancient civilisations, despite their differences, whether solar or lunar, and despite the passage of thousands of years since the beginning of the ancient Egyptian calendar that relied on the Nile flood to determine the beginning of the year is also the one that regulates agriculture in Egypt until now.
Researchers believe that the Egyptian calendar was founded by the ancient Egyptians and calculations were made according to the rotation of the sun, with the year divided into thirteen months, and despite the series of changes that affected it later, it is the most accurate until now due to the weather conditions as well as the different agricultural seasons.
Ancient egyptian calendar months
As for the four seasons, they are : The ‘Acht’ season, which in hieroglyphics means the horizon or the dawn of the sun, in which the land is prepared for planting and sowing, and includes 4 months, namely: The month of ‘Tut’ is attributed to the god Tut, the god of science and arts and the inventor of writing, then the month of ‘Baba’ to Hapi, the god of the Nile, the month of ‘Hathor’ and derives from ‘Hathor’ the sacred cow, the god of beauty and fertility, and the month of ‘Kihek’, then the season of ‘Bert’, which is the season of germination, and includes ‘Toba’, “Amshir”, “Barmahat”, and “Bermuda”, then “Shammu”, which is the season of harvest and drought, and includes “Bishnus”, “Buonah”, “Abib”, and “Masri”, thus making the Egyptian year consisting of 12 months, and each month is divided into 3 decimal groups with a total of 30 days.
















