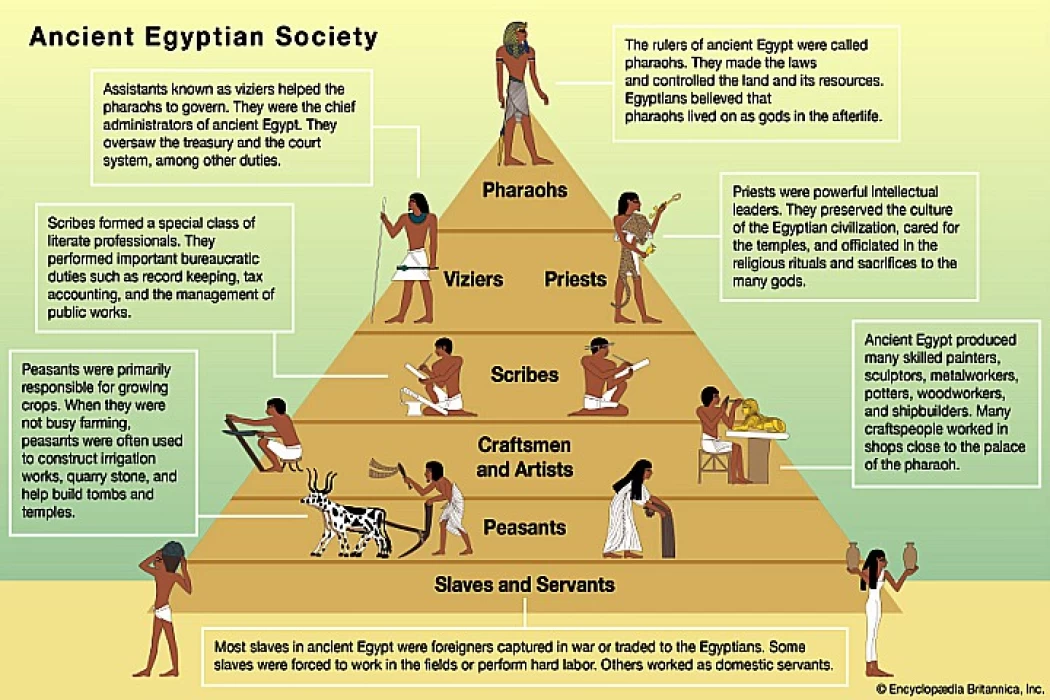
Ancient Egyptian Social Structure
Ancient Egyptian society during the Old Kingdom was divided into two classes, the upper class and the lower class, and these two types of classes were recognised by some sources in history such as the Dahshur Decree and the Epitaphs of Ipuwer.
However, at the end of the Old Kingdom, specifically during the reign of its last king, Bibi II of the Sixth Dynasty, the first social revolution took place. Thus, following the end of the old state and after the first social revolution, Egyptian society became divided into three classes:
1- The upper class
2- The middle class
3- The lower class.
If we consider that this class pyramid, as we think of it, holds the upper class that includes the king, the middle class that includes the scribes and state employees, and the lower class that includes the common people, this is considered a wrong social pyramid.
Because the ancient Egyptian king was not included in the upper class of the social pyramid, but the king was outside the class pyramid because the ancient Egyptian in the era of the ancient state was a deity. The lower class has been called ‘the broad base of the social pyramid. This is because it is the class on whose shoulders the ancient Egyptian civilisation was built.
The upper class: It is the first social pyramid and the class that enjoys the greatest prestige immediately after the king and includes all members of the royal family, including his wife, princes, and princesses, and then includes within this class - after the members of the royal family - The minister (who is currently considered the prime minister), provincial governors, and nobles such as high priests, high scribes, army commanders, and police commanders.
The middle class: This is the class that struggled to find a place between the upper and lower classes, which emerged following the end of the Old Kingdom, and included scribes, civil servants in the government sector, engineers, doctors, and skilled craftsmen doctors, skilled craftsmen (artists, sculptors), and labourers associated with the royal works, who were supposed to be placed in the lower class but became the middle class due to their proximity to the king.
The lower class: the lowest strata of ancient Egyptian society, on whose shoulders the ancient Egyptian civilisation was built. Whenever we are referring to the lower class, it is imperative for us to understand that the same class operates on a social pyramid with small employees at the apex and quarry workers at the base.
Rights and duties of the upper class: The upper class was entitled to stay in palaces, the right to educate their children, and the right to make huge tombs, in addition to having the right to be transported on coffins on the shoulders of men at the time, and their duties included
Exempt from taxes.
The rights and duties of the middle class: The middle class had the right to
to live in large houses and they also had the right to send their children to
schools, and they also had the right to make cemeteries, which was
the best of their rights and it was their duty to pay taxes.
Rights and duties of the lower class: They had no rights as they were
They lived in small houses and their children were not allowed to go to school
Also, they were not allowed to make large cemeteries, and their duties included
Their duties included paying taxes.
















