Sinai Peninsula
Experience the surprising beauty of the Sinai Peninsula.
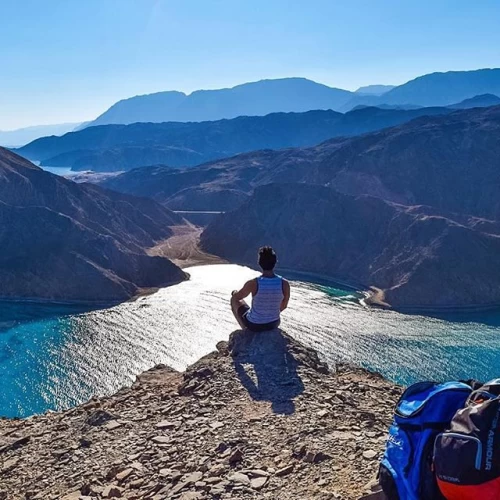
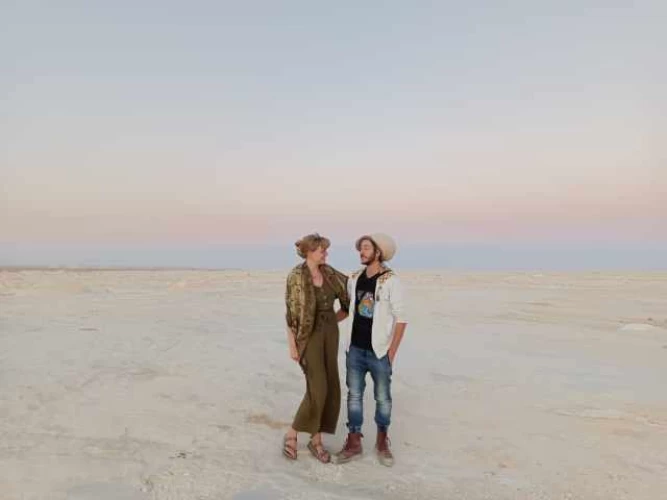
Sinai is a land of contrasts, the tranquil azure waters of the Red Sea against stark, rugged mountain ranges and vast deserts. It's the quintessential Egyptian land where Africa and Asia bridge face to a stunning panorama of natural beauty and historical significance given all the adventure options available.
A Geography Like No Other
It has a heart-capturing landscape that would leave no traveller indifferent aside from the golden beaches of Sharm El Sheikh and Dahab, where the turquoise, clear waters and colourful reefs make these places divers' and snorkelers' paradise. At the same time, the interior is torn between dramatic mountains and open spaces of desert, an invitation to all explorers to hike or camp and appreciate the peaceful beauty of wilderness.
Sinai Peninsula (Shibh Jazirat Sina')
The Sinai Peninsula, also called Turquoise Land, is a triangular desert peninsula that attracts many kinds of tourists to visit during their Egypt tours. Sinai region It is located in the northeastern part of the Arab Republic of Egypt, and it is the only part of Egypt that follows Asia geographically, with an area of about 60,000 km² (23,000 sq mi) and a population of approximately 1,400,000 people, representing 6% of Egypt's total area, and is bounded to the north by the Mediterranean Sea and to the west by the Gulf of Suez. Administratively, Turquoise Land is divided into two governorates: the South Sinai Governorate and the North Sinai Governorate. Three other governorates span the Suez Canal.
South Sinai
There is a clear ridge running along the southern edge of the Sinai in a large horseshoe curve. It is estimated that the Sinai desert receives more than 1.6 million acres (2 billion cubic meters) of water annually from local rain. About a quarter of this water flows on the surface as a bold flow, and a similar amount seeps into underground water tanks, providing excellent opportunities to conserve water. crossing into African Egypt: Port Said Governorate in the north, Ismailia Governorate in the centre, and Suez Governorate on the southern end of the Suez Canal.
Sinai has been inhabited since prehistoric times. The earliest written information about it dates back to 3000 B.C. during the early dynastic period of the 1st dynasty and the 2nd dynasty of Egyptian history, but it seems that the name Sinai was known early on and may have been derived from the original name for one of the oldest religious sects in the Middle East, the name of the moon. Its unique location, which overlooks the current lands (Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Israel, and Palestine), works on cultural rapprochement, and it has also worked on many disputes between Egypt and different countries, as the road has served the northern coast of Sinai as the main trade route between Egypt and Palestine for centuries.
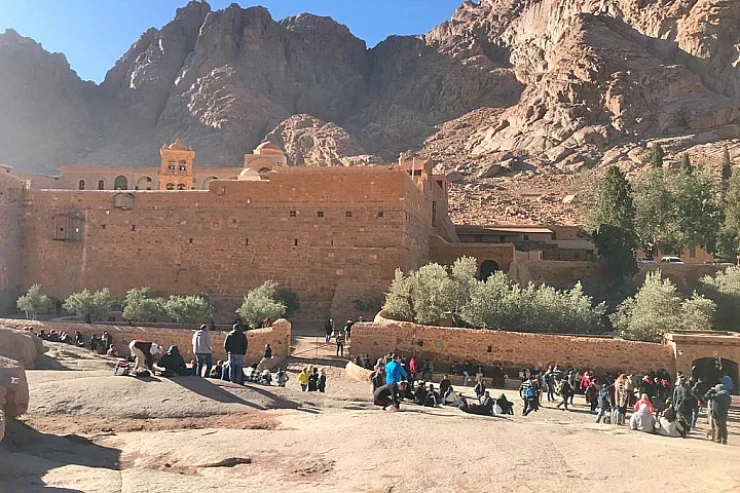
Mount Sinai
During the first Christian period, Sinai, Egypt, became home to a large number of hermits and ascetics, especially in the mountains of the southern region. In the year 530 A.D., Byzantine Emperor Justinian I began building the Monastery of Saint Catherine on the slopes of Mount Sinai. Since this provided a centre for Christian communities in the region, the monastery served as a pilgrimage site in the Middle Ages. Then the situation in Sinai deteriorated, and travel there became difficult after Egypt gained independence from direct Turkish rule in the early nineteenth century. Al-Arish was also the scene of fighting between the Turks and the British during World War I, and at the end of the war, Sinai was handed over to Egypt.
Between October 29, 1956, and March 30, 1957, Israel invaded and occupied the Sinai (the Triple Aggression in Egypt, as it was a simultaneous attack by the United Kingdom, France, and Israel), but on 6 October 1973 Egyptian forces did defeat Israel, and the northeastern part of the peninsula remained the scene of bitter fighting in 1956, 1967, and 1973. However, after a peace agreement between Egypt and Israel in late 1970, the Sinai Peninsula was returned to Egypt. This meant that in the aftermath of the peace treaty between Israel and Egypt in 1979, Israel withdrew from the Sinai Peninsula, with the exception of the disputed yet now settled Taba region, which had been reinstated after a jury ruling in 1989.
The Sinai Peninsula is a major tourist attraction with its natural location, rich coral reefs, and historic background. It is home to one of the most famous religious sites in Egypt: Mount Sinai has been the site of many religious pilgrimages. The population of this place was 597,000 as of January 2013. The other three governorates straddle the Suez Canal and seep into African Egypt: Suez (el-Sewais) is at the southern point of the Suez Canal, Ismailia (el-Isma'ileyyah) is at the centre, and Port Said is at the northern end.
The greatest city of Sinai is Arish, which is the capital of North Sinai and is populated by about 160,000 people. Other major settlements are Sharm el-Sheikh and El-Tor, which are located on the south coast. Inland Sinai is an arid (effectively desert) rugged mountain landscape in very sparsely populated areas, the greatest settlement being Saint Catherine and Nikhil.
Latest Articles
Admin
Seabourn Sojourn Cruise Stops in Safaga Port
The Seabourn Sojourn, the flagship vessel of Seabourn Cruise Line's ultra-luxury fleet, was built in 2008 at the T. Mariotti shipyard in Genoa, Italy. Measuring 198 metres, it can accommodate up to 450 guests in its 225 spacious all-suite staterooms.
Admin
Norwegian Sky Cruise Stops in Safaga Port
Norwegian Cruise Line operates a cruise ship called the Norwegian Sky. It was constructed in 1999 and can accommodate 2,004 passengers in addition to 878 crew members. The ship has several dining establishments, lounges and bars, a spa and fitness center, swimming pools, and a number of entertainment areas.
Admin
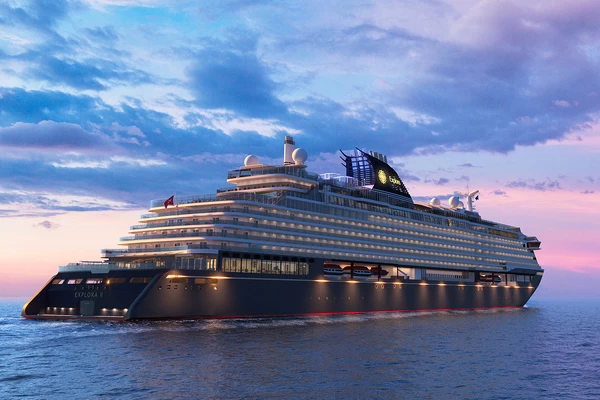
Explora II Cruise Stops in Safaga Port
Explora II, the second vessel in the Explora Journeys fleet, sets sail in 2024 to redefine luxury cruising. With 461 ocean-front suites, 9 culinary experiences, and 4 pools, this haven of sophistication and sustainability promises an unforgettable "Ocean State of Mind" journey to inspiring destinations.
Admin
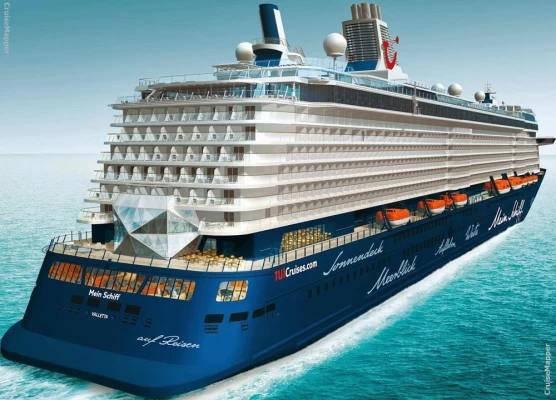
Mein Schiff 6 Cruise Stops in Safaga Port
The Mein Schiff 6 is the latest cruise ship in the renowned TUI Cruises fleet, offering passengers a luxurious and sophisticated cruise experience. At 315 metres long, this floating resort features a range of dining options, entertainment, and recreational facilities, including a spa, fitness centre, and sports amenities.
Admin
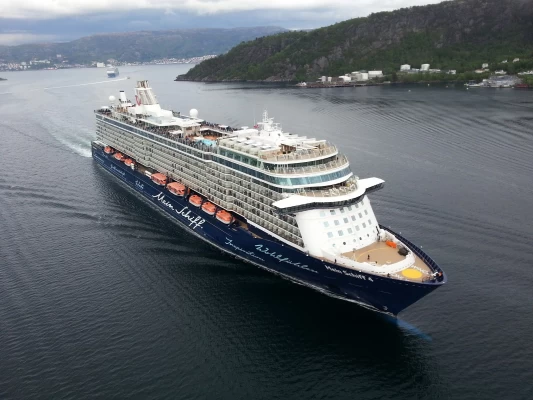
Mein Schiff 4 Cruise Stops in Safaga Port
When the Mein Schiff 4 cruise ship docks in Safaga, Egypt, passengers are granted access to a realm of ancient wonders. Aboard this state-of-the-art vessel, guests can embark on meticulously curated shore excursions that showcase the region's most iconic landmarks, including the Giza Pyramids, the enigmatic Sphinx, and the remarkable tombs and temples of the Valley of the Kings in Luxor.
Admin
MS Europa Cruise Stops in Safaga Port
The Silver Moon, Silversea's latest flagship, is a luxury cruise ship that offers an exceptional travel experience for Venezuelans exploring Egypt. With a capacity of 596 guests and an impressive 40,700 gross tonnes, the Silver Moon maintains the small-ship intimacy and spacious all-suite accommodations that are the hallmarks of the Silversea brand.











-webp.webp)







